In the past centuries, we saw an increase in deforestation activities such as cutting down trees for wood, extraction of natural resources, and clearing of forests to construct factories and houses. As a result of these activities, natural forests are decreasing at an alarming rate.
Forests provide a home to over 80% of terrestrial species of that world, oxygen to breathe, and maintain ecological balance by supporting biodiversity, moreover, they also provide essential resources and livelihoods for millions of people worldwide.
However, the health and sustainability of these vital ecosystems are increasingly under threat from deforestation, climate change, and unsustainable management practices. Governments worldwide, and independent organizations have taken notice of this and joined hands to counter deforestation and climate change. However, some hurdles stop this from happening.
About us: Viso Suite is the end-to-end computer vision platform. With Viso Suite, it becomes possible for enterprises to start using machine learning without a single line of code. Book a demo with us to learn more.
Forestry management is a difficult task and hence faces numerous challenges. As forest lands are vast and often inaccessible, they are labor-intensive and time-consuming, and manual data collection is extremely difficult, as a result accurately assessing forest conditions throws us with various challenges.
AI in forestry provides a way to transform and revolutionize how we monitor, manage, and protect our forests. By using satellite imagery, and drones, we can use computer vision to process and analyze visual data faster and at scale, leading to better forestry management.
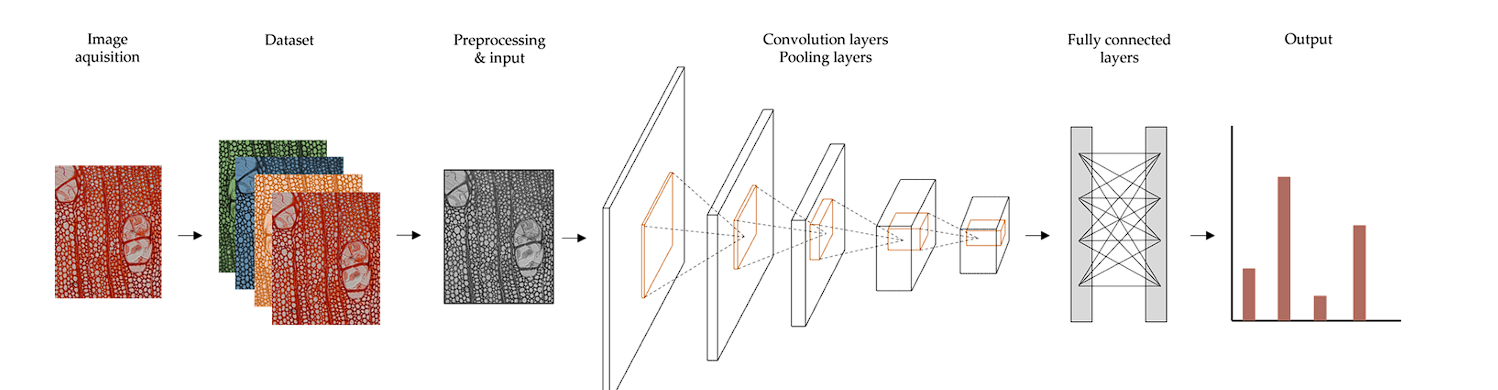
Analyzing Data from Drones
When drones are combined with high-resolution cameras and sensors, they can capture detailed images and videos of forested areas and go to places where it’s difficult for humans. By combining computer vision algorithms and drones we can:
- Monitor Forest Health: By analyzing (the color and texture of plants) in the pictures taken by drones, CV can be used to monitor the health of individual trees and detect signs of disease, pest infestations, and nutrient deficiencies.
- Estimate Tree Density and Biomass: By using AI in forestry, we can count the number of trees in a given area and estimate their biomass.
- Detect Illegal Logging: By comparing the latest drone footage with previously taken pictures, CV systems can automatically identify unauthorized logging activities and alert authorities to potential threats.
Leveraging Satellite Imagery
Satellites provide a top view of vast forested regions and capture images at regular intervals. These images combined with Computer Vision (CV) can help with:
- Tracking Deforestation: AI models can automatically detect changes in forest cover over time from satellite images. This provides statistical information that helps with informed decision-making in identifying areas where deforestation is happening and assists with creating effective strategies for conservation efforts.
- Map Forest Types and Biodiversity: By analyzing the spectral signatures of different tree species, CV applications can create detailed maps of forest composition and biodiversity.

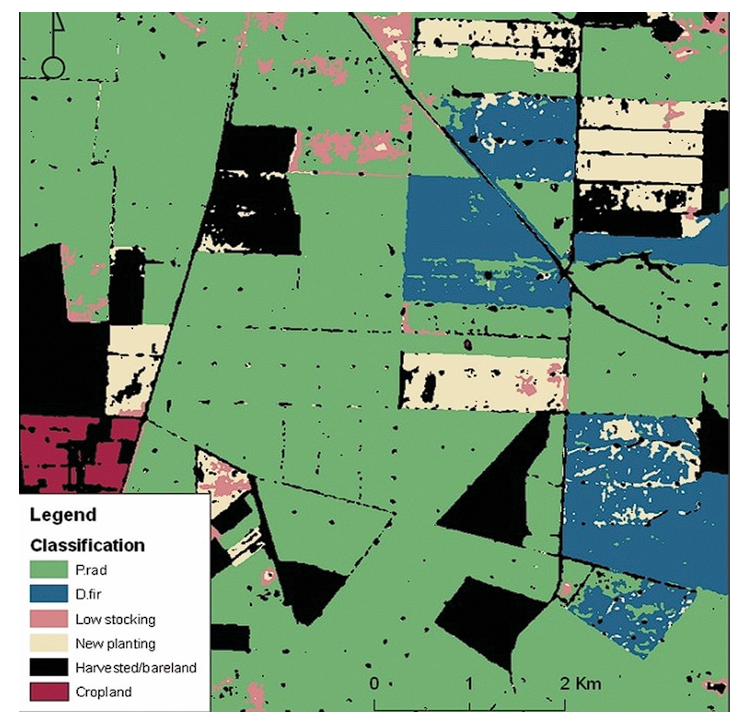
Classification of harvested areas, new plantings, and areas of low stocking using satellite imagery –source - Monitor Forest Fires: CV can detect the early signs of forest fires, such as smoke and heat signatures, which enables providing rapid response and minimizing damage.
Ground Vehicles
Unmanned Ground Vehicle (UGV), when equipped with cameras and sensors, can navigate through forests, and capture detailed images and data from the forest floor. Computer vision applications then use this data to:
- Assess Understory Vegetation: CV can analyze the density and composition of the underlying layer of vegetation in a dense forest or wooded area vegetation. This is often difficult for humans to reach but is possible with UGV.
- Measure Tree Growth: The captured images of tree trunks and branches can measure tree growth rates and monitor the impact of environmental factors on forest development.
- Identify Invasive Species: CV can help with detecting and identifying invasive plant species.
Key Applications of AI in Forestry
1. Tree Species Identification
Different tree species have varying ecological roles, attributes, growth rates, wood qualities, economic values, and conservation statuses. As a result, identifying tree species is a crucial part of forestry solutions.
Drones fly over forested areas and capture detailed images of tree canopies from various angles. Then, researchers process these images using computer vision algorithms to detect features such as leaf shape, color, texture, and branching patterns.
Moreover, researchers use special cameras equipped with spectral and hyperspectral imaging capabilities to identify species based on their species-specific spectral signatures.
2. Forest Inventory and Analysis
Using computer vision, researchers automate the process of counting trees. This provides a detailed inventory of forest resources and tracks changes in their numbers, which helps assess afforestation or deforestation.
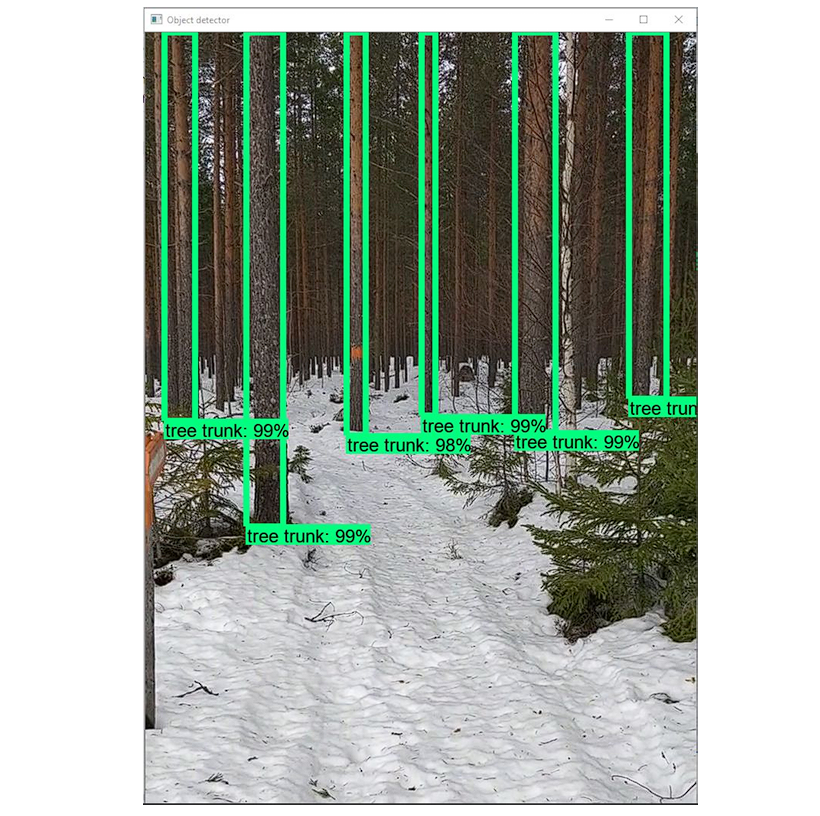

Moreover, we can also perform:
- Health Assessment: By analyzing the color and texture of leaves and bark, researchers can detect different diseases, including pest infestations and nutrient deficiencies in trees.
- Size Measurement: Measure the height and diameter of trees from images.
- Volume Estimation: We can utilize Lidar data from drones or planes to create detailed 3D maps of forest structure, tree height, and density. This is valuable for natural resource management and carbon stock assessments.
- Mapping: Researchers can use remotely sensed images from satellites to create detailed maps of forest composition, tree density, and species distribution.
3. Wildlife Monitoring
Using object detection algorithms in forestry AI, we can identify, and count wildlife species present in a forest. Moreover, we can also perform:
- Behavior Analysis: Analyzing video footage to study animal behaviors and movements.
- Habitat Mapping: Mapping habitat features.
4. Sustainable Forest Health Monitoring
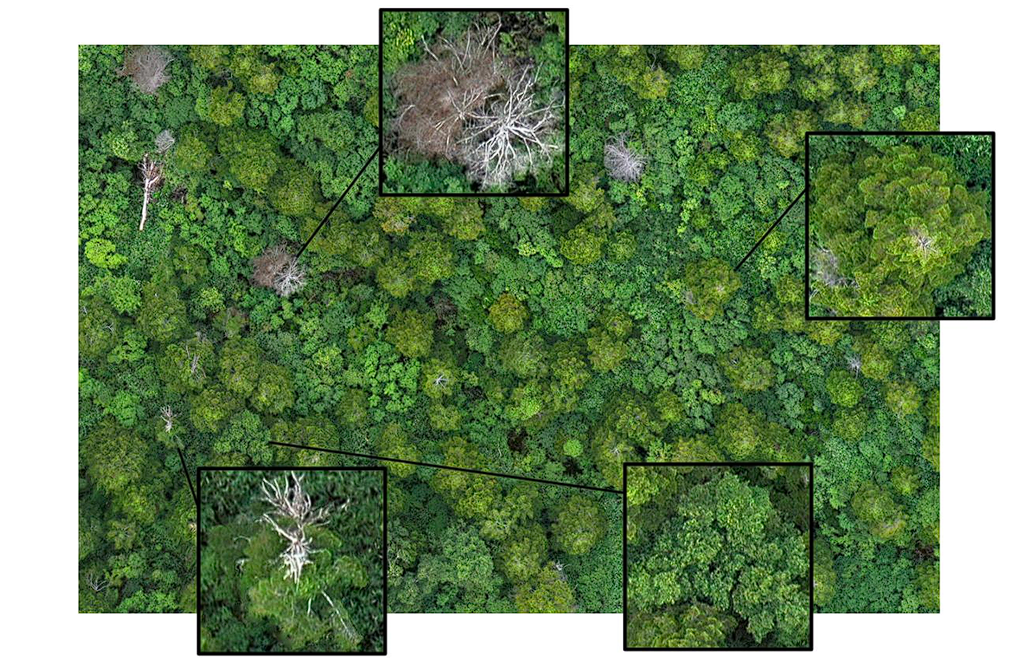

Forests are vulnerable to various threats such as diseases, pest infestations, and environmental damage. Early detection and intervention are essential for prevention and conservation.
A wide range of sensors coupled with drones and satellites capture high-resolution images of forest canopies and help with health analysis. The data gathered is then fed to state-of-the-art CV models (YOLO, EfficientNet, MobileNet) to detect signs of disease and pest infestations:
- Color Analysis: Changes in leaf color may indicate health issues. Yellowing or browning leaves are usually signs of disease or nutrient deficiencies.
- Texture Analysis: Abnormal textures, such as holes or spots on leaves, can indicate pest damage.
- Pattern Recognition: Irregular patterns in trees, such as defoliation or dieback, can be signs of health problems.
- Detect Fungal Infections: Ground-based imagery from vehicles and sensors can detect fungal growth on tree trunks and roots.
- Monitor Soil Health: Sensors can measure soil moisture and nutrient levels; this can be used to provide automated alerts.
- Thermal Imaging: Infrared cameras are used to detect temperature anomalies in tree canopies, indicating stress or disease.

Near-infrared band assisting in highlighting the differences in crop vigor –source - NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index): By calculating NDVI from satellite or drone images using spectral imaging, we can assess vegetation health and detect early signs of diseases.
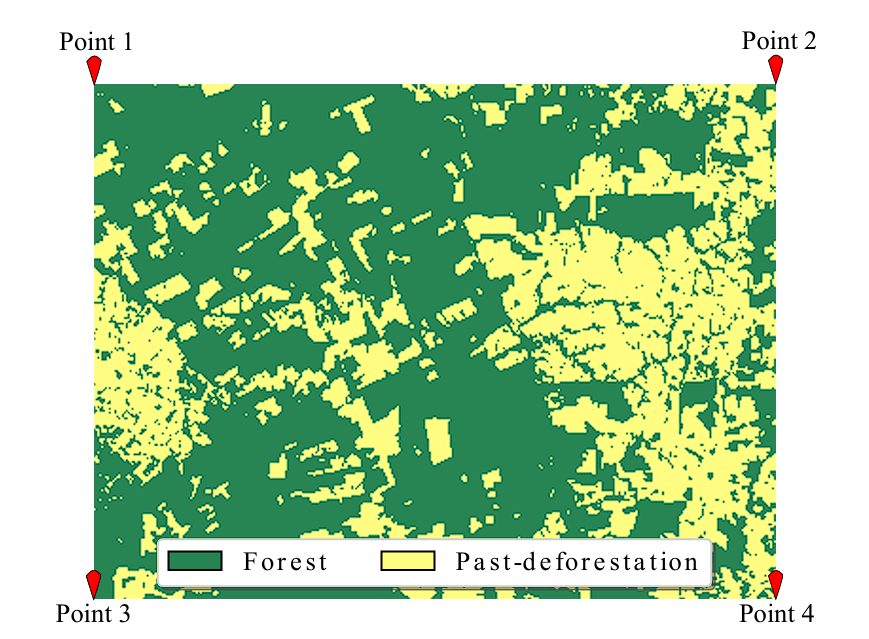
5. Deforestation Detection and Prevention
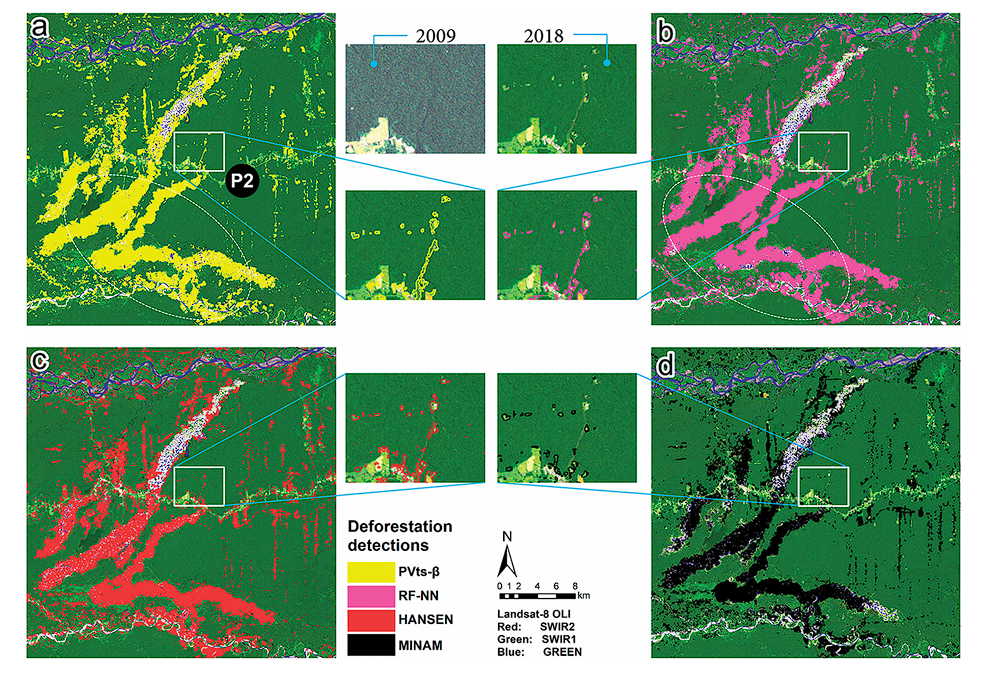
Deforestation has an impact on global forests, which results in loss of biodiversity, disruption of ecosystems, and contribution to climate change through increased carbon emissions. The adverse effects of climate change are visible all around the globe, with increased sea levels, irregular rains, increased forest fires, and unexpected weather changes.
All these can be prevented by reducing deforestation. The use of AI in forestry drastically helps with controlling deforestation by detecting illegal logging.
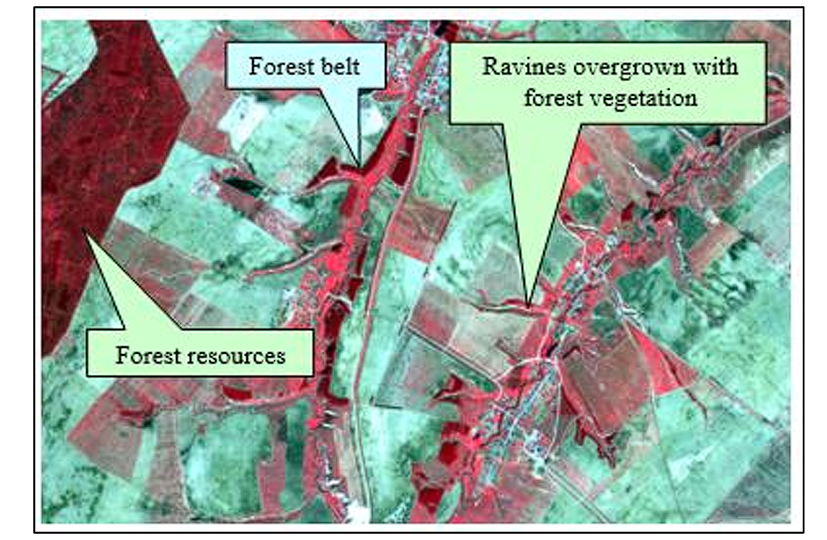
The images of forests captured by satellites at regular intervals provide a continuous stream of data and monitoring. These images are then fed to AI models that analyze the images to detect changes in forest cover.
One of the major problems encountered is illegal deforestation. The application of AI in forestry can detect anomalies in forest cover to help prevent illegal activities such as forest clearing or burning.
These systems offer real-time monitoring of forest cover changes, as they generate alerts when suspicious activities are detected. This enables authorities to take swift action against illegal activities.
6. Biomass Estimation and Carbon Sequestration
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities. These greenhouse gases lead to global warming and hence climate change. Plans absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere and store it in the form of biomass. As a result, forests play a crucial role in carbon storage and climate regulation by reducing the amount of greenhouse gas in the atmosphere.
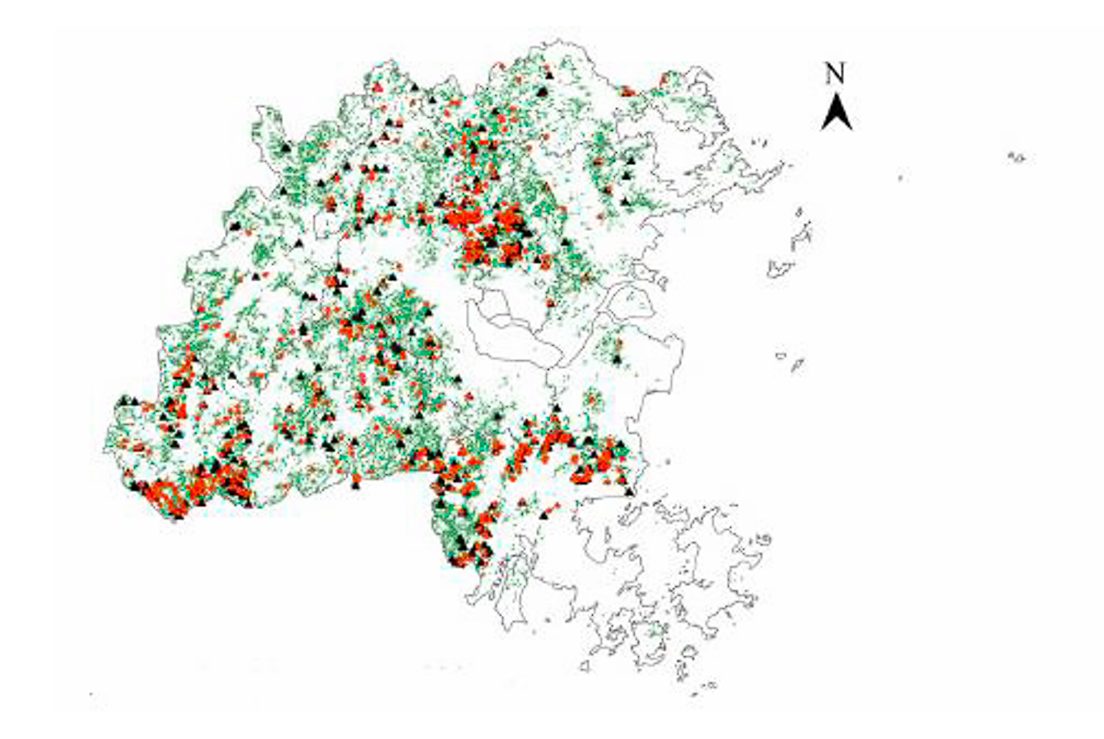
Accurate estimation of forest biomass and carbon sequestration is crucial for climate change prevention, as they have a direct impact. Biomass and carbon sequestration data play an important role in shaping policy decisions and international agreements related to carbon credits and emissions reductions.
Computer Vision performs this. By combining CV models with LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) technology, we can precisely estimate forest biomass and carbon storage.
LiDAR sensors use laser pulses to create detailed 3D maps of forest structures. By mounting this sensor on drones or aircraft, researchers can capture data on tree height, canopy density, and forest floor topography.
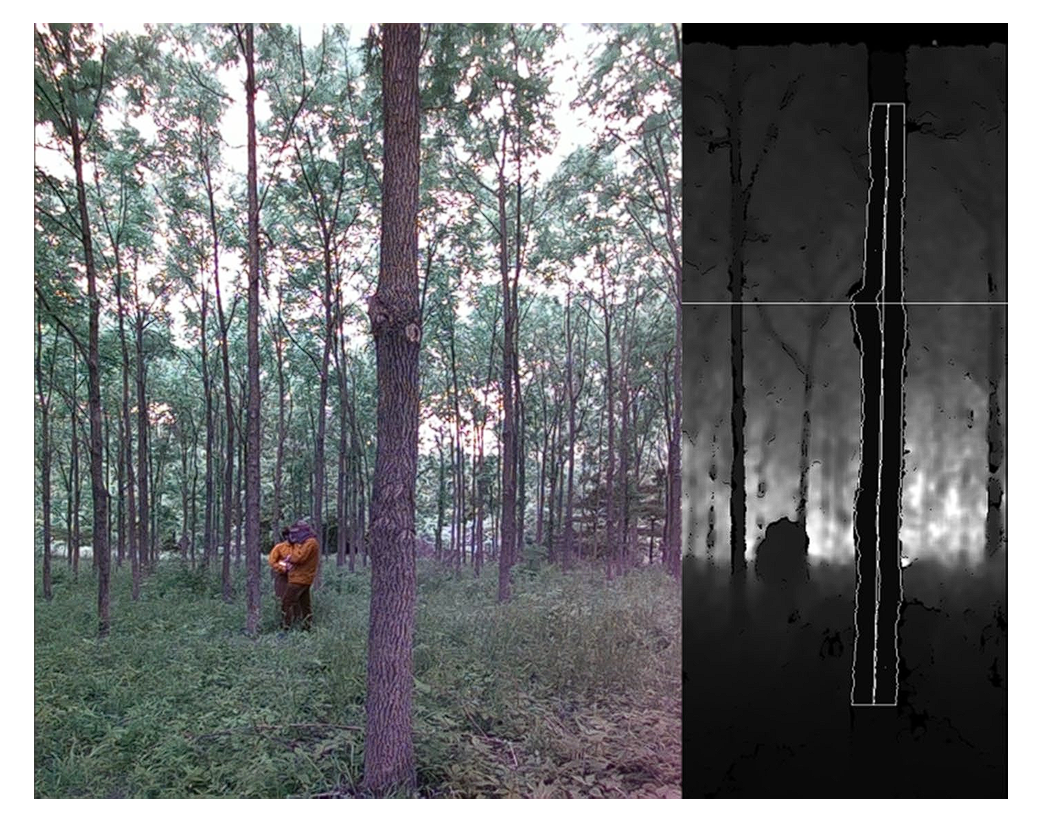

CV models process the LiDAR data to estimate biomass and carbon storage using:
- 3D Modeling: Creating 3D models of individual trees and forests to calculate their volume and biomass.
- Forest Growth Monitoring: We can use satellite or drone imagery to monitor and model forest growth, and biomass changes.
- Canopy Analysis: Analyzing canopy structure and density to estimate the amount of carbon stored in the forest. Moreover, researchers can use NDVI indices to estimate vegetation health and carbon absorption rates.
7. Wildfire Detection and Forest Management
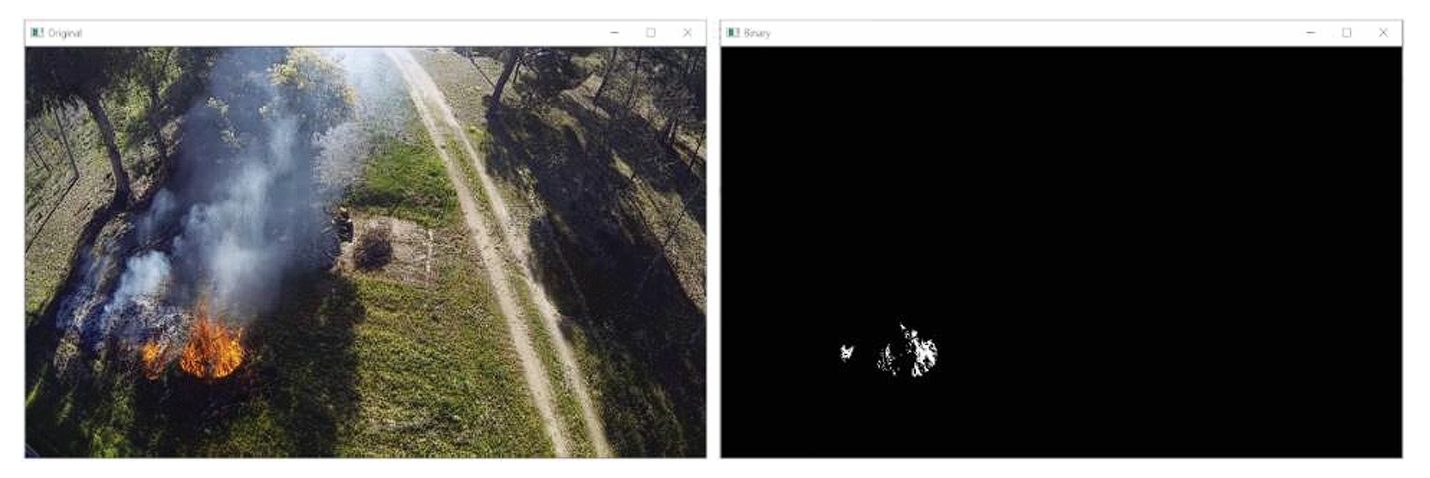
The number of wildfires has been increasing recently due to climate change, prolonged droughts, and emissions by human activities. Wildfires are a threat to not only the forests, but also the animals, and humans living nearby. Computer vision combined with thermal imaging and real-time monitoring systems using drones and satellites is the solution for reducing and managing wildfires.
These systems continuously monitor forested areas for signs of wildfires using heat detection. Thermal imaging can identify hotspots and areas where temperature increases in the forests, this can indicate the possibility of wildfires. Moreover, infrared images can also be used to detect smoke and plumes in the air.
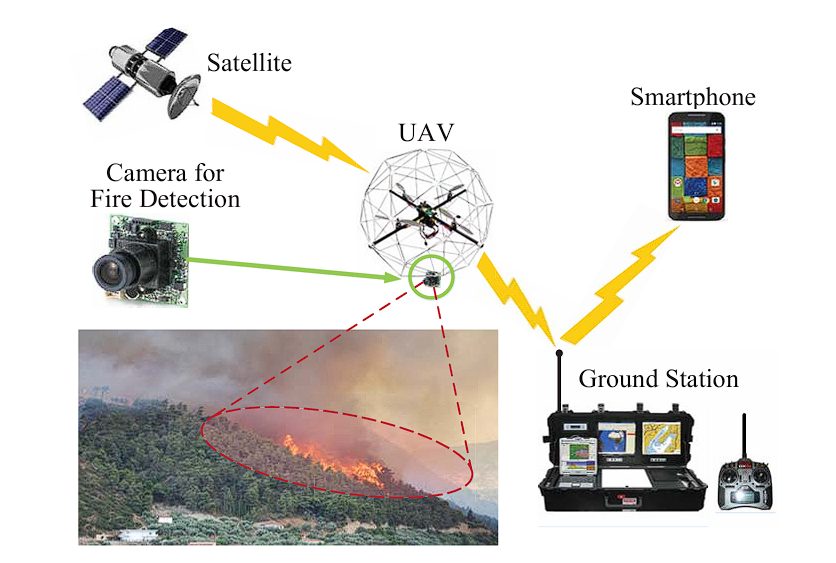
Moreover, CV can also be used for fire predictions.
- Predictive Modeling: Real-time data from thermal and regular cameras can be combined with weather data to predict fire spread patterns.
- Simulation: We can also create simulations from real-time data by using fire behavior simulation models, this improves the prediction accuracy.
8. Soil Erosion Conservation
We can identify areas prone to erosion by analyzing topographical changes from Lidar sensor data. Moreover, by using AI in forestry and multispectral imaging we can monitor soil health.
9. Seedling Detection and Monitoring
- Automated Detection: We can use image recognition to detect and count seedlings in reforestation areas.
- Growth Monitoring: By using time-lapse photography, we can monitor the growth of the seedling and its survival rates.
Conclusion
In this blog, we looked at the different practical applications of Computer Vision in forestry management. We saw how AI in forestry is revolutionizing the way we monitor and protect our forests. When coupled with drones, LiDAR sensors, multispectral imaging, and satellite images, CV can be used for tree species identification, forest inventory analysis, health monitoring of trees, Deforestation Detection and Prevention, and Biomass Estimation.
As Artificial Intelligence (AI) continues to advance, we can expect more useful and accurate tools for monitoring and managing our forests. These innovations will enable us to address the pressing challenges of deforestation, climate change, and biodiversity loss more effectively. Moreover, organizations such as the World Resources Institute (WRI), created in the United States are relentlessly working towards a more sustainable future.
Read our other blogs to learn more about the applications of AI in different industries and sectors:
- 9 Applications of Computer Vision in Law and Legal Systems
- Computer Vision In Manufacturing: The Most Popular Applications in 2024
- 16 Applications of Computer Vision in Construction (2024 Guide)
- High-value Applications of Computer Vision in Oil and Gas (2024)
- Top Applications of Computer Vision in Insurance (2024 Guide)